|
Size: 11826
Comment: copy, to be translated
|
← Revision 6 as of 2009-12-25 07:11:03 ⇥
Size: 11172
Comment: converted to 1.6 markup
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 5: | Line 5: |
| [[TableOfContents]] 原文 [http://wiki.wxpython.org/index.cgi/ModelViewPresenter wxPython wiki :: ModelViewPresenter] |
<<TableOfContents>> 原文 [[http://wiki.wxpython.org/index.cgi/ModelViewPresenter|wxPython wiki :: ModelViewPresenter]] |
| Line 10: | Line 10: |
| == Foreword == ModelViewPresenter is a derivative of the ModelViewController Pattern. Its aim is to provide a cleaner implementation of the Observer connection between Application Model and view. For more information about this pattern check [http://c2.com/cgi/wiki?ModelViewPresenter] and [http://www.martinfowler.com/eaaDev/ModelViewPresenter.html]. The original Taligent article is still available at [http://www.oodesign.com.br/forum/index.php?act=Attach&type=post&id=74]. There is also a paper titled "Presenter First" at [http://atomicobject.com/media/files/PresenterFirst.pdf], which presents a pattern and process for test-driven development (TDD) of GUI apps structured with MVP. (Caveat: I've only briefly scanned the paper, and don't know whether it will warrant the link on closer inspection. -- Don Dwiggins) Most of the following information is an adaptation of Martin Fowler's MVP page to wxPython. A lot of the text is just Copy&Paste. == Introduction == Model View Presenter separates the behavior of the presentation out into a separate presenter class. Any user events are forwarded to the presenter and the presenter manipulates the state of the view. As well as separating the responsibilities, this also allows the behavior to be tested without the UI, and for different UI controls to be used with the same basic behavior. == How It Works == The heart of Model View Presenter is to pull all the behavior of the presentation out of view and place it in a separate presenter class. The resulting view will by very dumb - little more than a holder for the gui controls themselves. In this way the separation is very much the same as the classic separation of Model View Controller. The difference between MVC and MVP is that in MVP the presenter does not handles the GUI events directly as the controller does in MVC but through delegation via the interactor. This in my view allows easier testing of the presenter. == Example: Album Window == Here is an example: inline:mvp.png The code for model is just a simple data object. |
= 前言 = ModelViewPresenter 是ModelViewController模式的一个派生产物。其目的是提供一个Observer连接(模型与视图)的整洁实现方法。此模式更多信息可以参考 [[http://c2.com/cgi/wiki?ModelViewPresenter]] 和 [[http://www.martinfowler.com/eaaDev/ModelViewPresenter.html]]。原始文章请看 [[http://www.oodesign.com.br/forum/index.php?act=Attach&type=post&id=74]]。而 [[http://atomicobject.com/media/files/PresenterFirst.pdf]] 这篇文章展示了使用MVP来构建GUI程序测试驱动开发(TDD)的模式和过程。(Caveat: I've only briefly scanned the paper, and don't know whether it will warrant the link on closer inspection. -- Don Dwiggins) 接下来的大部分信息来源于Martin Fowler's MVP页面,但经调整可用于wxPython。很多文字仅仅是复制和粘贴而来。 = 简介 = Model View Presenter 将表现行为分离出来,形成单独的presenter类。所有用户事件都被转向presenter,由presenter处理视图(view)的状态。在分离任务的同时,它也允许在没有UI的清况下测试这些行为,允许对不同的UI使用相同的基本行为。 = 如何运作 = Model View Presenter 的核心是将所有的presentation行为从view中分离出来,并放置到单独的presenter类中去。最终得到的view是几乎没有能动性的 - 除了保持GUI控件。这种方式的分离和经典的Model View Controller分离是非常相似的。 MVC与MVP的差别在于MVP中presenter不像MVC的controller那样直接处理GUI事件,而是利用interactor,通过delegation来实现。在我看来,这使得presenter的测试更加容易。 = 示例: Album Window = {{attachment:mvp.png}} 模型代码仅是简单的数据对象。 |
| Line 45: | Line 41: |
| You start the application by creating a presenter. | 通过创建presenter来启动程序。 |
| Line 59: | Line 55: |
| The View is built inside a wx.Frame | View在wx.Frame内构建 |
| Line 71: | Line 67: |
| Before instantiating the Frame we create the wx.App object used by our application and when the view starts we start the Main Loop. In real life you could create the layout using something like wxGlade and inherit one of the generated classes. The presenter is responsible for putting all the data into the window. It does this by pulling data out of the domain class and pushing the data into the window via the view interface. |
将Frame实例化之前,我们创建应用程序的wx.App对象,当view启动时,我们开始Main Loop。在实际工作中,你可以使用wxGlade之类的工具创建布局,并从生成的类中进行继承。 presenter负责把所有的数据放入窗口。它从主类中获取数据,并通过view的接口将数据置入窗口。 |
| Line 110: | Line 106: |
| The loadViewFromModel method updates all the items of view. Some of these updates cause events to fire which would cause a recursive trigerring of the update method, so I use a guard around the update method to prevent the recursion. The methods in the view allow access to the underlying controls via the fields. |
loadViewFromModel方法对view中所有项目进行更新。有一些更新事件会导致递归式的触发更新方法,所以在这里我使用对更新方法加入一个防护,防止递归的发生。 view中的方法允许通过fields访问下层的控件。 |
| Line 124: | Line 120: |
| Alternatively the view could be implemented using property objects and use simple assignment/access instead of set/get methods. | 除了set/get方法之外,view还可以使用对象属性以及通过简单的assignment/access方法来实现。 |
| Line 136: | Line 132: |
| then | 接下来 |
| Line 151: | Line 147: |
| The interactor object is installed from the presenter and it installs all the needed event handlers delegating the event to the presenter. | interactor对象从presenter被安装,它安装所有必需的event handler, 这些handler将event委托给presenter。 |
| Line 177: | Line 173: |
| You save data to the model when the user hits the apply button. | 当用户点击apply按钮时,将数据保存到model。 |
| Line 193: | Line 189: |
| To test if apply works you can use the unittest module and mock objects for view and interactor | 要检查apply是否正常工作,你可以使用unittest模块,模仿view和Interactor对象。 |
| Line 210: | Line 206: |
| Complete implementation together with mock objects and tests: inline:mvp.zip To start the application use albums.pyw == Expanding applications with MVP architecture == Let's say that the next step would be to add the capability to add new albums and to provide a way to sort the albums either ascending or descending. The application will look like this: inline:mvp2.png The best order to expand the example is to start in the test module and first update the tests, next the presenter, the mock views, then when the functionality is done move to the real view, add the necessary bits and then alter the interactor to connect the view with the presenter. For expediency reasons will do it first the View next the Presenter and last the Interactor. First let's add the visual bits: In the AlbumWindow we add 2 buttons, place them beneath the albums list and provide access to the order button label. |
完整的实现(包括模仿对象和测试): [[attachment:mvp.zip]] 使用 albums.pyw 运行程序。 = 使用MVP构架扩展应用程序 = 假设下一步要增加功能:增加新的albums,提供将albums按照升/降方式来排序的方法。此程序应该看起来是这个样子: {{attachment:mvp2.png}} 扩展这个例子的最好顺序是:从测试模块开始,首先升级测试,然后是presenter,模仿的views,然后,当这些功能完整移植到真正的view中之后,增加必须的部分并替换interactor来连接view和presenter。方便起见,从View开始,然后Presenter,最后Interactor。 首先增加可视部分: 在AlbumWindow中增加两个按钮,放置于albums列表的下方,并提供访问排序按钮标签的方法。 |
| Line 242: | Line 239: |
| Next we add the functionality in the presenter. First we add a flag to hold the order: | 接下来,在presenter中增加相应功能。首先,增加标记来保存顺序(order): |
| Line 253: | Line 250: |
| Next we fix the refreshAlbumList method to take into account that the list must be sorted according to our selected order. | 接下来,考虑到应该根据我们选择的顺序对列表排序,对refreshAlbumList方法进行修改: |
| Line 283: | Line 280: |
| Now all that remains to be done to update the AlbumInteractor to provide the connection between button presses and our new functionality: | 剩下要做的就是更新AlbumInteractor,提供按钮点击和新功能之间的连接: |
| Line 300: | Line 297: |
| All Done! New version of the source code: inline:mvp2.zip Remember! When writing production code start in the unittests, this way you'll be able to catch logic related errors early on, before they are altered by the view part. }}} |
全部完成! 新版的源代码: [[attachment:mvp2.zip]] 记住!编写产品代码时,从unittests开始,这样你就可以在相关的逻辑错误被view部分替换之前,尽早的发现它们。 |
Contents
原文 wxPython wiki :: ModelViewPresenter
即将翻译,标记一下
1. 前言
ModelViewPresenter 是ModelViewController模式的一个派生产物。其目的是提供一个Observer连接(模型与视图)的整洁实现方法。此模式更多信息可以参考 http://c2.com/cgi/wiki?ModelViewPresenter 和 http://www.martinfowler.com/eaaDev/ModelViewPresenter.html。原始文章请看 http://www.oodesign.com.br/forum/index.php?act=Attach&type=post&id=74。而 http://atomicobject.com/media/files/PresenterFirst.pdf 这篇文章展示了使用MVP来构建GUI程序测试驱动开发(TDD)的模式和过程。(Caveat: I've only briefly scanned the paper, and don't know whether it will warrant the link on closer inspection. -- Don Dwiggins)
接下来的大部分信息来源于Martin Fowler's MVP页面,但经调整可用于wxPython。很多文字仅仅是复制和粘贴而来。
2. 简介
Model View Presenter 将表现行为分离出来,形成单独的presenter类。所有用户事件都被转向presenter,由presenter处理视图(view)的状态。在分离任务的同时,它也允许在没有UI的清况下测试这些行为,允许对不同的UI使用相同的基本行为。
3. 如何运作
Model View Presenter 的核心是将所有的presentation行为从view中分离出来,并放置到单独的presenter类中去。最终得到的view是几乎没有能动性的 - 除了保持GUI控件。这种方式的分离和经典的Model View Controller分离是非常相似的。
MVC与MVP的差别在于MVP中presenter不像MVC的controller那样直接处理GUI事件,而是利用interactor,通过delegation来实现。在我看来,这使得presenter的测试更加容易。
4. 示例: Album Window
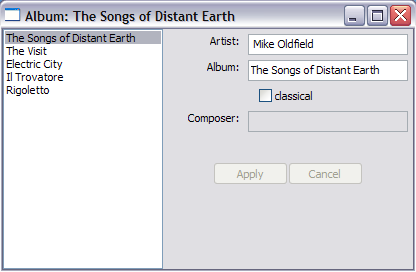
模型代码仅是简单的数据对象。
通过创建presenter来启动程序。
View在wx.Frame内构建
将Frame实例化之前,我们创建应用程序的wx.App对象,当view启动时,我们开始Main Loop。在实际工作中,你可以使用wxGlade之类的工具创建布局,并从生成的类中进行继承。
presenter负责把所有的数据放入窗口。它从主类中获取数据,并通过view的接口将数据置入窗口。
1 class AlbumPresenter(object):
2 ...
3 def loadViewFromModel(self):
4 if self.isListening:
5 self.isListening = False
6 self.refreshAlbumList()
7 self.view.setTitle(self.selectedAlbum.title)
8 self.updateWindowTitle()
9 self.view.setArtist(self.selectedAlbum.artist)
10 self.view.setClassical(self.selectedAlbum.isClassical)
11 if self.selectedAlbum.isClassical:
12 self.view.setComposer(self.selectedAlbum.composer)
13 else:
14 self.view.setComposer("")
15 self.view.setComposerEnabled(self.selectedAlbum.isClassical)
16 self.enableApplyAndCancel(False)
17 self.isListening = True
18
19 def refreshAlbumList(self):
20 currentAlbum = self.view.getSelectedAlbum()
21 self.view.setAlbums(self.albums)
22 self.view.setSelectedAlbum(currentAlbum)
23 self.selectedAlbum = self.albums[currentAlbum]
24
25 def updateWindowTitle(self):
26 self.view.setWindowTitle("Album: " + self.view.getTitle())
27
28 def enableApplyAndCancel(self, enabled):
29 self.view.setApplyEnabled(enabled)
30 self.view.setCancelEnabled(enabled)
31 ...
loadViewFromModel方法对view中所有项目进行更新。有一些更新事件会导致递归式的触发更新方法,所以在这里我使用对更新方法加入一个防护,防止递归的发生。
view中的方法允许通过fields访问下层的控件。
除了set/get方法之外,view还可以使用对象属性以及通过简单的assignment/access方法来实现。
接下来
interactor对象从presenter被安装,它安装所有必需的event handler, 这些handler将event委托给presenter。
1 class AlbumInteractor(object):
2 def Install(self, presenter, view):
3 self.presenter = presenter
4 self.view = view
5 view.albums.Bind(wx.EVT_LISTBOX, self.OnReloadNeeded)
6 view.title.Bind(wx.EVT_TEXT, self.OnDataFieldUpdated)
7 view.artist.Bind(wx.EVT_TEXT, self.OnDataFieldUpdated)
8 view.composer.Bind(wx.EVT_TEXT, self.OnDataFieldUpdated)
9 view.classical.Bind(wx.EVT_CHECKBOX, self.OnDataFieldUpdated)
10 view.apply.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.OnApply)
11 view.cancel.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.OnReloadNeeded)
12
13 def OnApply(self, evt):
14 self.presenter.updateModel()
15
16 def OnReloadNeeded(self, evt):
17 self.presenter.loadViewFromModel()
18
19 def OnDataFieldUpdated(self, evt):
20 self.presenter.dataFieldUpdated()
当用户点击apply按钮时,将数据保存到model。
1 def updateModel(self):
2 self.selectedAlbum.title = self.view.getTitle()
3 self.selectedAlbum.artist = self.view.getArtist()
4 self.selectedAlbum.isClassical = self.view.isClassical()
5 if self.view.isClassical:
6 self.selectedAlbum.composer = self.view.getComposer()
7 else:
8 self.selectedAlbum.composer = None
9 self.enableApplyAndCancel(False)
10 self.loadViewFromModel()
要检查apply是否正常工作,你可以使用unittest模块,模仿view和Interactor对象。
1 class TestAlbumPresenter(unittest.TestCase):
2 ...
3 def testApplySavesDataToModel(self):
4 view = mock_objects.MockAlbumWindow();
5 model = [models.Album(*data) for data in self.someAlbums]
6 interactor = mock_objects.MockAlbumInteractor()
7 presenter = presenters.AlbumPresenter(model, view, interactor);
8 newTitle = "Some Other Title"
9 view.title = newTitle
10 presenter.updateModel()
11 assert view.title == newTitle
完整的实现(包括模仿对象和测试): mvp.zip 使用 albums.pyw 运行程序。
5. 使用MVP构架扩展应用程序
假设下一步要增加功能:增加新的albums,提供将albums按照升/降方式来排序的方法。此程序应该看起来是这个样子:
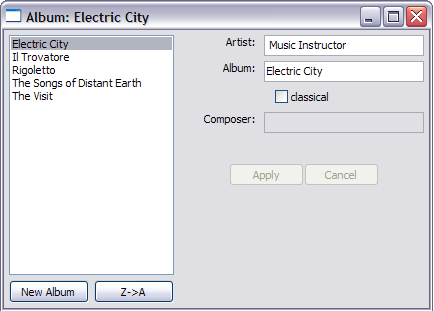
扩展这个例子的最好顺序是:从测试模块开始,首先升级测试,然后是presenter,模仿的views,然后,当这些功能完整移植到真正的view中之后,增加必须的部分并替换interactor来连接view和presenter。方便起见,从View开始,然后Presenter,最后Interactor。
首先增加可视部分:
在AlbumWindow中增加两个按钮,放置于albums列表的下方,并提供访问排序按钮标签的方法。
1 class AlbumWindow(wx.Frame):
2 def __init__(self):
3 ...
4 self.add = wx.Button(self, label="New Album")
5 self.order = wx.Button(self, label="A->Z")
6
7 leftSizer = wx.GridBagSizer(5,5)
8 leftSizer.Add(self.albums, (0,0), (1,2),flag=wx.EXPAND)
9 leftSizer.Add(self.add, (1,0), (1,1),flag=wx.EXPAND)
10 leftSizer.Add(self.order, (1,1), (1,1),flag=wx.EXPAND)
11 ...
12 mainSizer.Add(leftSizer, 0, wx.EXPAND|wx.ALL, 5)
13 ...
14 def setOrderLabel(self, label):
15 self.order.SetLabel(label)
接下来,在presenter中增加相应功能。首先,增加标记来保存顺序(order):
接下来,考虑到应该根据我们选择的顺序对列表排序,对refreshAlbumList方法进行修改:
1 class AlbumPresenter(object):
2 def refreshAlbumList(self):
3 currentAlbum = self.view.getSelectedAlbum()
4 self.selectedAlbum = self.albums[currentAlbum]
5 self.albums.sort(lambda a, b:self.order*cmp(a.title, b.title))
6 self.view.setAlbums(self.albums)
7 self.view.setSelectedAlbum(self.albums.index(self.selectedAlbum))
Provide a way to toggle the order and a way to add a new album
1 class AlbumPresenter(object):
2 def toggleOrder(self):
3 self.order = -1*self.order
4 self.loadViewFromModel()
5
6 def addNewAlbum(self):
7 newAlbum = models.Album("Unknown Artist", "New Album Title")
8 self.albums.append(newAlbum)
9 self.view.setAlbums(self.albums)
10 self.view.setSelectedAlbum(self.albums.index(newAlbum))
11 self.loadViewFromModel()
剩下要做的就是更新AlbumInteractor,提供按钮点击和新功能之间的连接:
1 class AlbumInteractor(object):
2 def Install(self, presenter, view):
3 ...
4 view.add.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.OnAddNewAlbum)
5 view.order.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.OnToggleOrder)
6
7 def OnAddNewAlbum(self, evt):
8 self.presenter.addNewAlbum()
9
10 def OnToggleOrder(self, evt):
11 self.presenter.toggleOrder()
全部完成!
新版的源代码: mvp2.zip
记住!编写产品代码时,从unittests开始,这样你就可以在相关的逻辑错误被view部分替换之前,尽早的发现它们。
